As consumers, we often take the availability of fresh food and medication at our local stores for granted. However, behind the scenes, a complex process is involved in ensuring that these products are transported and stored at the right temperature. This process is known as the cold chain, and it’s essential for maintaining the quality and safety of certain foods, beverages, and medications.
The global supply chain relies on the cold chain, which accounts for approximately 20-25% of the worldwide supply in 2021.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the cold chain’s details, how it works, and the challenges involved in maintaining it.
Understanding cold chain

Proper temperature control is crucial for preserving the quality of goods in the cold chain. Transporting temperature-sensitive goods in uneven temperatures can result in the loss of millions of goods.
What is a cold chain?
Cold chain is a term used to describe the process of transporting and storing temperature-sensitive goods, such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals, in a temperature-controlled environment, from production to consumption.
Its management aims to maintain the integrity and quality of the product throughout the entire supply chain. This involves using specialised equipment, such as refrigerated trucks, warehouses, and containers, to keep the product within a specific temperature range. Failure to maintain the temperature-controlled supply chain can result in spoilage, degradation, or even product contamination, seriously affecting public health and safety.
What is cold chain logistics?
Cold chain logistics involves all the organisational processes that ensure the smooth and efficient functioning of the cold chain. Its goal is to ensure that products reach their destination in the same condition they were in when they left the sender.
What are examples of cold chains?
Cold chain products include perishable and temperature-sensitive items like ice cream and vaccines. Maintaining the right temperature and environment throughout the cold supply chain is crucial to prevent spoilage and ensure public safety. Here are examples of products that require specific temperature conditions:
1. Vaccines and medical products (between 2°C and 8°C)
As the world grappled with the COVID-19 pandemic, the need for efficient transportation of vaccines became increasingly important. Cold chain logistics is the process of transporting vaccines and other medical products such as blood, biologics, insulin, and medical devices at specific temperature ranges to maintain their efficacy.
This method is utilised by leading manufacturers such as Pfizer and Moderna to ensure their vaccines are delivered to people worldwide safely. The demand for cold chain logistics has never been higher than during the pandemic period, so it’s essential to have reliable and efficient cold logistics.
2. Food – perishable meat, seafood, poultry (0°C and 5°C)
When it comes to transporting food, temperature control is crucial. If perishable items like meat, seafood, and poultry aren’t kept at stable temperatures throughout the entire cold chain process, they can quickly become a breeding ground for harmful bacteria. This can lead to food poisoning and other serious health risks.
To ensure the safety and quality of food supply, it’s essential always to prioritize proper temperature control during transportation.
3. Fresh and frozen fruits and vegetables, icy desserts (fresh – between 0°C and 5°C / frozen – below -18°C)

The cold chain and logistics are crucial in ensuring that fresh and frozen fruits and vegetables are available daily in our local supermarkets.
These products require specific temperature control during transportation to prevent damage, bacterial growth, flavour loss, and bruising, which can lead to unnecessary wastage.
Also, icy desserts require specific temperatures to remain frozen and enjoyable. This intricate system ensures we have access to the freshest and highest quality produce possible while reducing food waste and promoting sustainability.
4. Dairy products (0°C and 5°C)
Keeping dairy products fresh and safe for consumption requires a well-maintained cold chain. This involves appropriately storing and transporting products such as milk, cheese, and yoghurt at a consistent temperature from production to consumption.
Also, it’s essential to purchase dairy products from reputable sources.
5. Wine (between 10°C to 20°C)

When it comes to wine, the taste and quality are everything. And if you’ve ever wondered how that bottle of wine made it to your table or a friend’s birthday party, you should know that it’s all thanks to the cold chain and logistics.
Wine must be stored at cool temperatures to prevent premature ageing and loss of flavour. The cold chain ensures that the wine is transported and stored in temperature-controlled environments to maintain its quality.
From the winery to the distributor to the retailer, every step of the way, the cold chain is crucial for ensuring that your wine arrives at the perfect temperature and ready to be enjoyed. So the next time you raise a glass of wine, you can thank the cold chain for making it possible.
Four elements of the cold chain

The cold chain has many moving parts. However, there are four main elements:
1. Cold storage
Cold storage facilities are responsible for safe freight storage before shipping to distant markets. Proper cold storage management ensures that the goods remain fresh and high-quality during transit. By maintaining optimal temperatures and humidity levels, cold storage facilities help to prevent spoilage and ensure the delivery of safe, fresh goods to the end consumer.
2. Cold transportation
Cold transportation ensures that the goods arrive at their destination in optimal condition. That’s why choosing the right transportation provider that understands the importance of proper temperature control and has the necessary equipment to handle your specific needs is of utmost importance.
3. Cooling system
It’s essential to have cooling systems in place throughout the entire cold chain process. Whether it’s during processing, storage, or transporting goods, these systems ensure that the products reach their destination in optimal condition. By prioritising the quality of cooling systems, your freight can be handled with utmost care and precision.
4. Cold processing and distribution
Cold processing ensures that the goods are handled in a sanitary manner, preserving their quality and preventing contamination. While cold distribution involves carefully loading and transporting the goods, ensuring they remain at the correct temperature throughout the journey.
Cold chain operations

Temperature-controlled supply chain operations encompass a series of operations for transporting freight. These synchronised operations maintain the temperature level throughout all the cold chain stages:
-
Temperature monitoring and control
Maintaining proper temperature control is crucial in any supply chain, but it’s especially important in the cold one. Temperature monitoring and control systems ensure that products such as food, pharmaceuticals, and other sensitive goods remain at the proper temperature throughout the logistics process.
One way to monitor temperature in a cold chain is by using sensors, data loggers, or smart devices. These tools can record, transmit, and notify stakeholders of any temperature changes. Additionally, the data gathered by these devices can be used to analyze the performance of the cold chain, pinpoint the source of any issues, and enhance the overall efficiency and dependability of the process.
-
Packaging and insulation
Packaging is a critical aspect of the cold supply chain and it’s necessary to maintain the desired temperature range and protect the products from external factors. The packaging can include various forms, such as:
- cold chain parcel and pallet systems;
- gel packs and gel bottles;
- dry ice;
- refrigerant bricks;
- insulated containers and envelopes.
The packaging must comply with relevant regulations and standards, including ISTA and WHO guidelines.
-
Transportation

For transportation, a global cold chain supply has various transportation options. These include global or local roads and highways, the air, rail, and across waterways. Notably, there is an unquestionable demand for specialised refrigerated vehicles.
KleverCargo is a freight exchange platform for road transport where you can find reliable carriers who handle perishable goods and have suitable vehicles to control temperature, ensuring the safe movement of goods.
The process of posting perishable goods and creating transport requests is simple and user-friendly, taking only a few steps:
1. Log in to your KleverCargo account, select +Create new and choose the Transport request option.
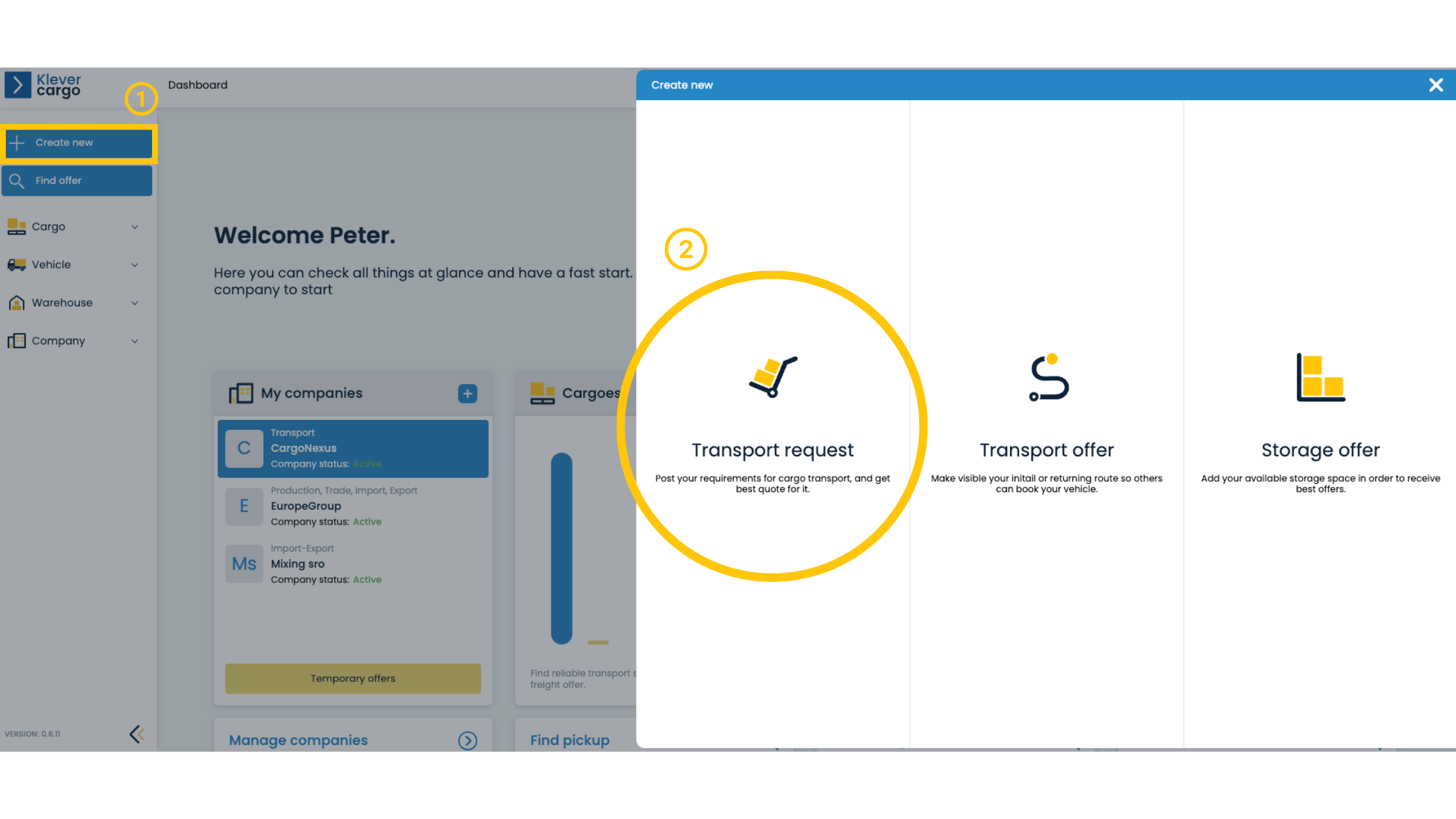
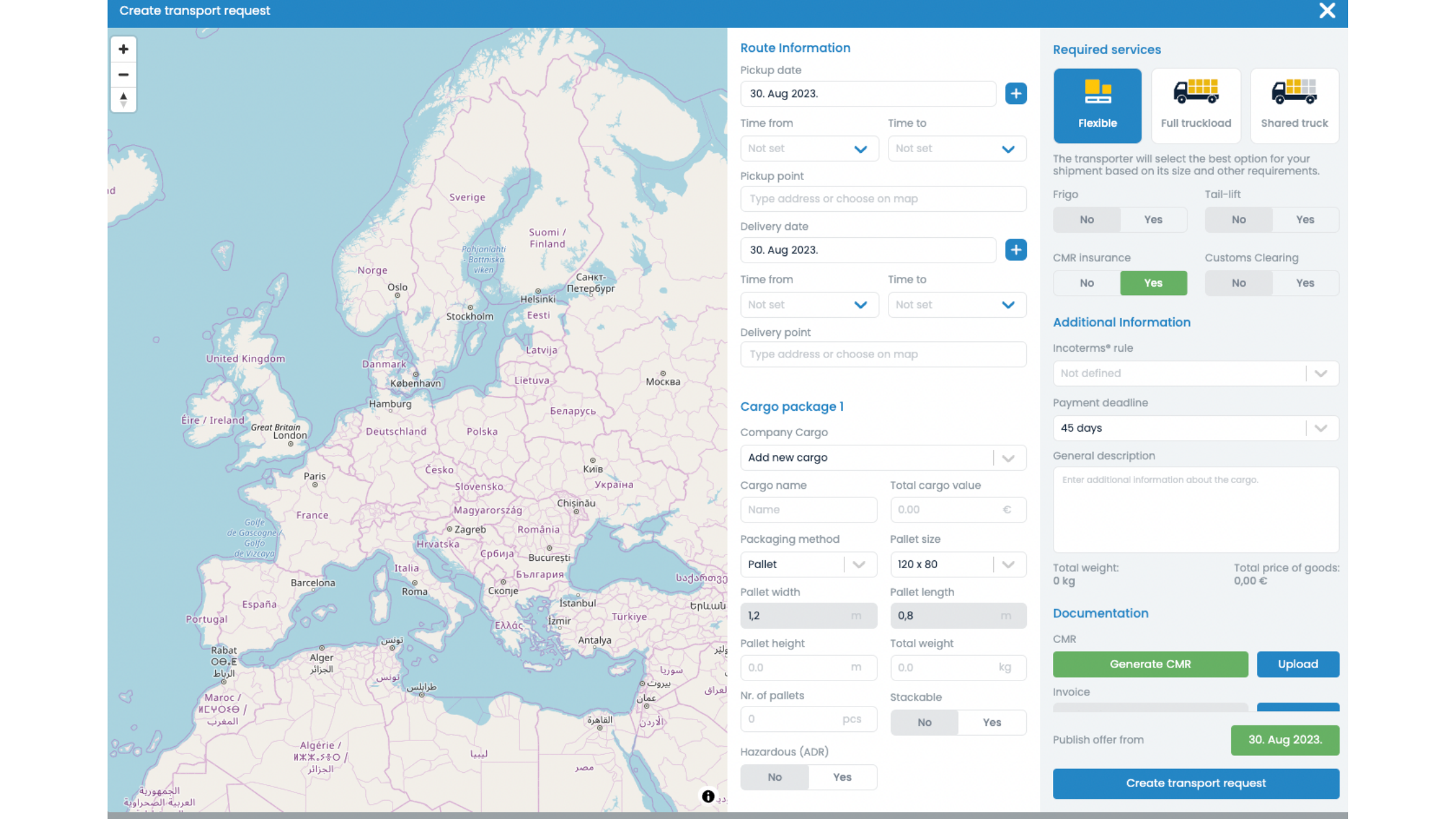
2. You will be prompted to enter all necessary information about the route and cargo in a new window.
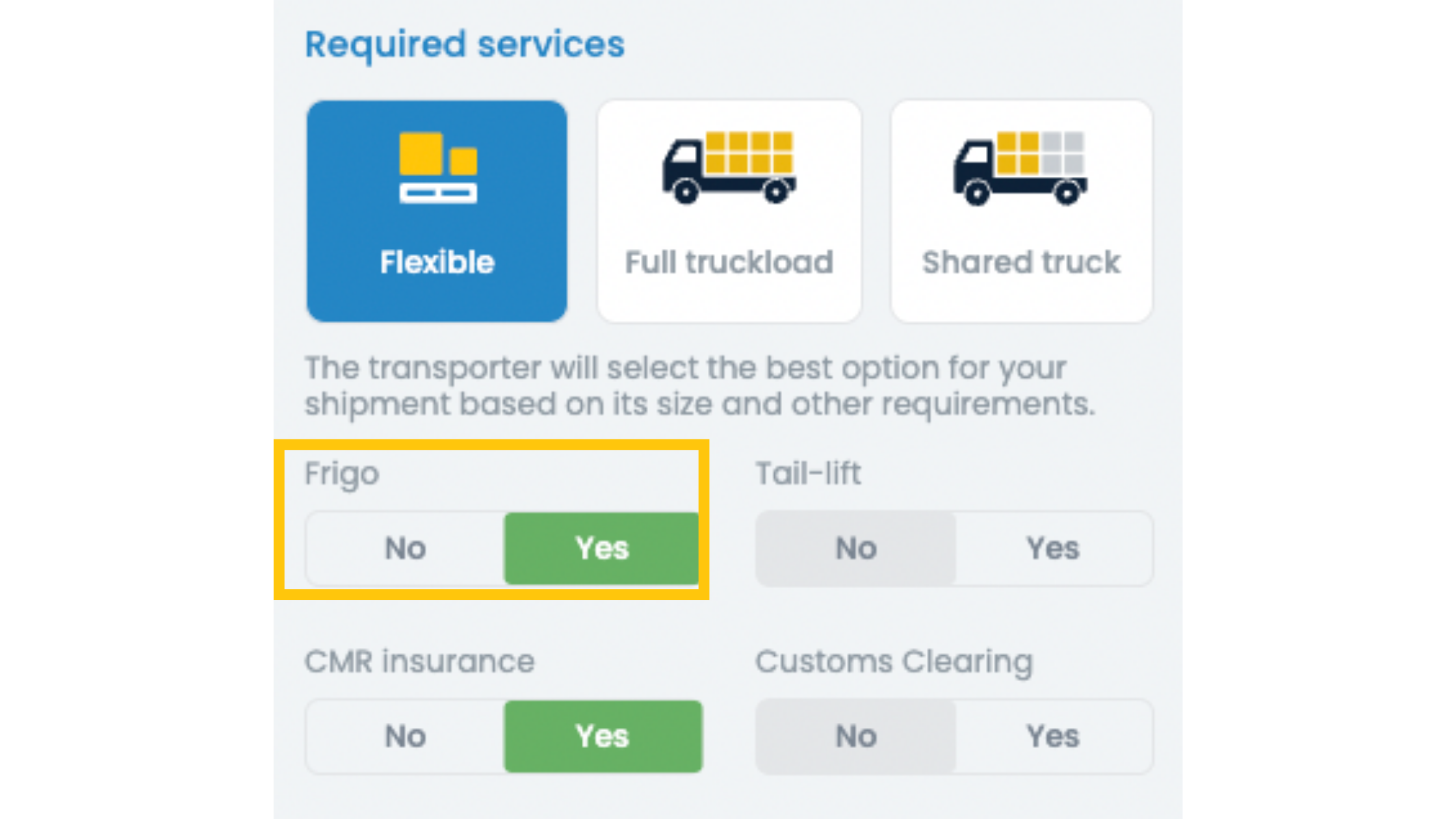
3. You can find one crucial feature for perishable goods. It’s the option under Required services, specifying that you need a FRIGO vehicle.
4. Additionally, if you have any further requirements, you can utilise the available space to ensure that all information is included.
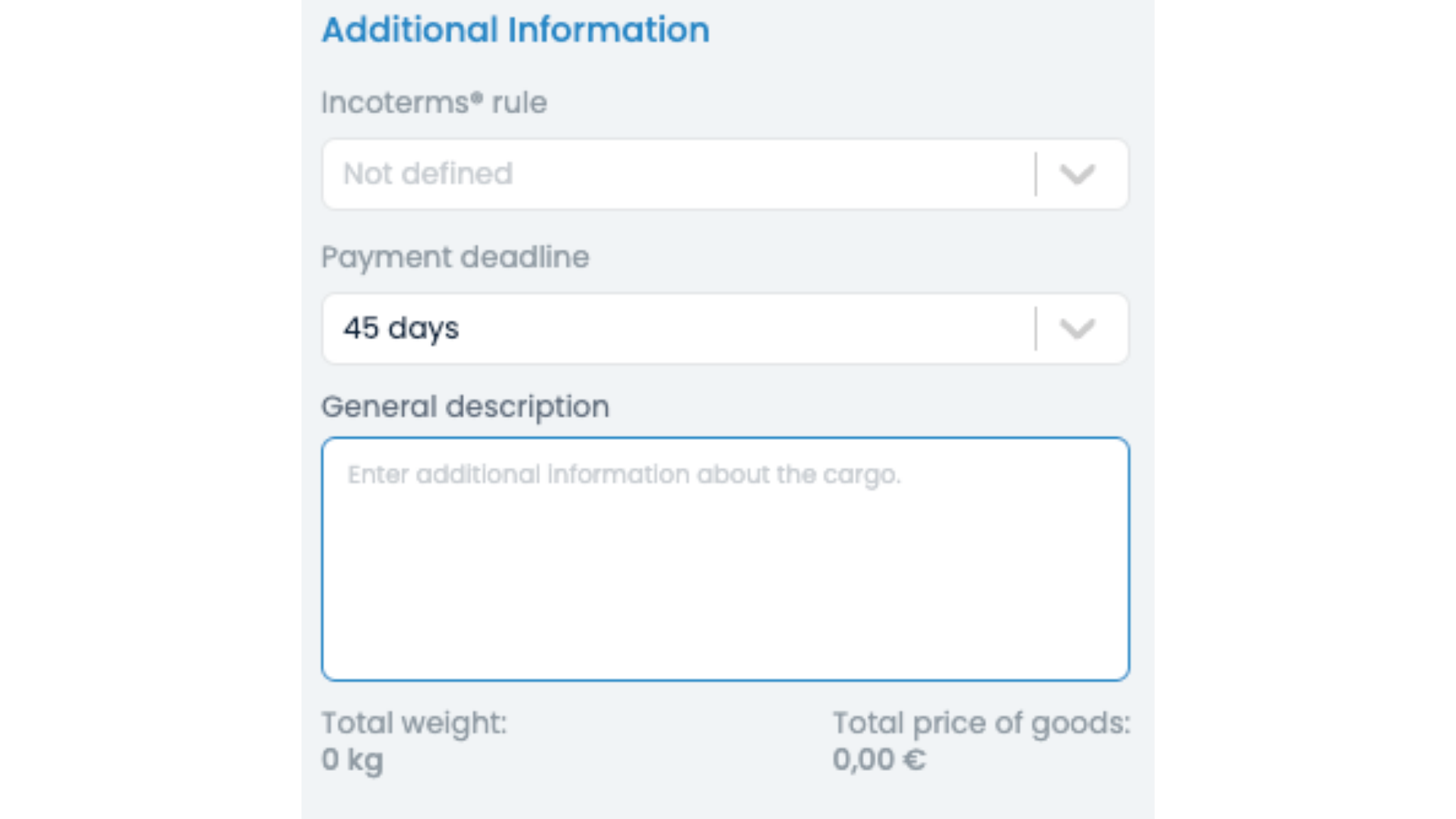
5. Now there is only left to click Create transport request, and that’s it, simple as that.
What is the risk of a cold chain?

It’s important to account for the risks involved in the cold chain process. Despite the best efforts, certain factors may be beyond our control. However, backup plans can mitigate these risks. Potential risks include:
1. Equipment failure
One of the main risks associated with maintaining a cold chain is the possibility of equipment failure. This can occur for various reasons, with power interruptions being one of the most common causes.
When a blackout occurs, the cooling systems can fail, resulting in significant damage to a refrigerated truck that relies on a single source of electricity. Moreover, inadequate air circulation in storage rooms can expedite the deterioration of temperature-sensitive goods.
It’s important to conduct regular checks on vents and spots to prevent incidents. Also, always have an accumulator available to avoid potential consequences of a blackout.
2. Environmental factors
Environmental factors can pose a risk when it comes to cold chain supply. This includes the shipment’s destination and the weather conditions it will encounter. For instance, some regions may subject the cargo to extreme heat or cold. Using a reefer with its own power source can help alleviate these concerns.
Another important consideration is managing the atmospheric conditions within the cold chain. This involves regulating oxygen and carbon dioxide levels, which are crucial for slowing down the ripening process of the cargo. It’s typical to encase the products in polyethylene bags during transport to achieve this. These bags help control the permeability of gases and ensure a controlled atmosphere for the products throughout the refrigerated transportation system.
3. Delayed pickups or deliveries
Cold chain logistics involves many moving parts. Due to this, delayed pickups or deliveries due to various occurrences are a risk. They can happen because of accidents on the road or staff shortages.
Also, because of high demand surges and issues with regulatory compliances. Besides these, cross-border customs clearances and miscommunication in coordination also affect this issue.
4. Quality control
When it comes to maintaining a high level of quality control in cold chains, it’s crucial to ensure that all freight and vehicles are adequately sanitised, cleaned, and sorted before packaging and loading.
By prioritising sanitation and adhering to the shipper’s recommended guidelines, we can ensure that the entire process is carried out most effectively.
5. Human error
Human errors can often disrupt the cold chain. Common reasons for human errors include insufficient training and improper packaging. Also, use of equipment and doing things in a rush.
Try to decrease the potential for human error with proper training of employees.
Future cold chain trends

With global tech advancements, there are some cold chain trends we expect to take place in the future. They include innovations in temperature monitoring and control. Furthermore, in blockchain technology and integrations of IoT. A lot of things are already happening.
-
Innovations in temperature monitoring and control
There are many advancements in temperature monitoring and control within the cold chain. These include cloud-based monitoring platforms, radio frequency identification, artificial intelligence, and thermal imaging.
These innovations are currently being utilized at a basic level, but engineers are already working on developing their full potential for the future.
-
Blockchain technology
With the help of blockchain technology, it’s possible to track the temperature history and condition of freight throughout the whole process from transportation to end consumer. This ensures the authenticity and quality of products and provides valuable data that can be used to improve the cold chain.
-
Integration of IoT
IoT sensors and devices are becoming more popular in the temperature-controlled supply chain industry. They help track the temperature and environmental conditions by attaching them to shipping containers, trucks, or even individual products.
The data they collect is transferred to a central platform in real-time, allowing continuous monitoring. Thanks to IoT technology, any temperature changes can be quickly detected and addressed.
In summary
The cold chain plays a crucial role in the global supply by ensuring the quality of products. It’s essential to maintain all elements of its operations to avoid compromising the integrity of the products. As technology advances, we’ll likely see even more efficient and effective cold chain systems in the future.
Take advantege of the technology right now and register on the KleverCargo platform to find suitable transportation for your temperature-sensitive freight. Here is a YouTube tutorial to help you register.


